Overall Architecture
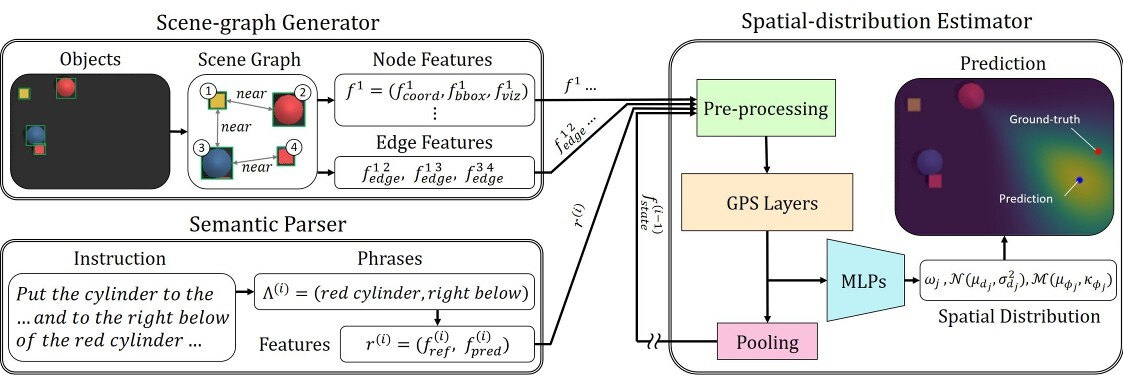
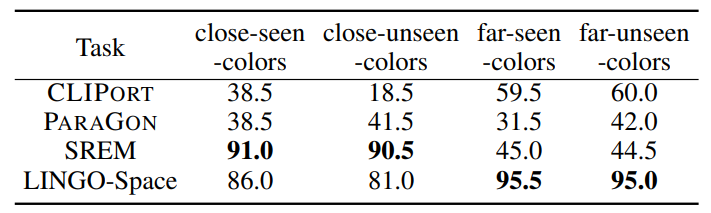
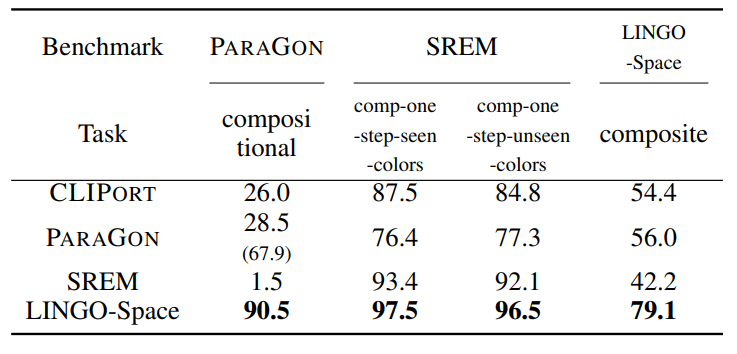
We aim to solve the problem of spatially localizing composite instructions referring to space: space grounding. Compared to current instance grounding, space grounding is challenging due to the ill-posedness of identifying locations referred to by discrete expressions and the compositional ambiguity of referring expressions. Therefore, we propose a novel probabilistic space-grounding methodology (LINGO-Space) that accurately identifies a probabilistic distribution of space being referred to and incrementally updates it, given subsequent referring expressions leveraging configurable polar distributions. Our evaluations show that the estimation using polar distributions enables a robot to ground locations successfully through $20$ table-top manipulation benchmark tests. We also show that updating the distribution helps the grounding method accurately narrow the referring space. We finally demonstrate the robustness of the space grounding with simulated manipulation and real quadruped robot navigation tasks. Code and videos are available at https://lingo-space.github.io.


@inproceedings{kim2024lingo,
title={LINGO-Space: Language-Conditioned Incremental Grounding for Space},
author={Kim, Dohyun and Oh, Nayoung and Hwang, Deokmin and Park, Daehyung},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
volume={38},
number={9},
pages={10314--10322},
year={2024}
}